Application of Buccal smear for detection of Cytological changes Of Hormonal Therapy
- Gharb El-Niel College-Sudan
- Ahfad University for Women, Sudan
Abstract
Background: Cancer-related mortality is high in Sudan, with low survival rates attributed to advanced-stage disease at presentation. This study aimed to assess hormonal therapy-induced cytological changes in buccal mucosa among Sudanese women with breast and endometrial cancers.
Methods: This community-based, quantitative study evaluated cytological changes in buccal smears from women undergoing hormone therapy in Khartoum State. Fifty patients receiving hormone therapy were included. Buccal smears were collected from participants and prepared using wet-fixation and air-dried methods for staining with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E).
Results: Cytological analysis revealed malignant changes in 56% of cases, inflammatory changes in 34%, and normal findings in 10%. Results were comparable between wet-fixation and air-dried methods. Smear quality for the wet method was rated as excellent (40%), very good (28%), good (20%), acceptable (8%), and poor (4%); similar quality distributions were observed for the dry method. No significant differences in cytological findings (P = 0.14) or smear quality (P = 0.11) were observed between preparation methods. However, cytological abnormalities significantly correlated with duration and frequency of hormone therapy (P = 0.001).
Conclusion: Buccal smears from women undergoing hormone therapy predominantly exhibited malignant cytological changes, followed by inflammatory and normal findings. Preparation method (wet vs. dry) did not significantly influence outcomes.
Introduction
Chemotherapy and radiation are the most widely used interventions for the treatment of cancer1, 2, 3, 4. Oral complications that arise with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy induce many disorders represented in many scientific reports2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) has long been recognized as a method of treatment for adverse symptoms resulting from the cessation of ovarian endocrine function10. Most patients in Sudan receive high and repeated doses of hormonal replacement therapy. This study was designed to assess the changes in buccal smears induced by hormonal replacement therapy among Sudanese women with breast and endometrial cancers. The study aimed to compare between wet fixed and air-dry Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stained buccal smear samples in diagnosing buccal cytology changes for the detection of buccal cytology changes due to hormonal therapy among Sudanese women with breast and endometrial cancers.
Methods
This was a community-based, quantitative study to assess the cytological changes in buccal cavity smears among patients undergoing hormone replacement therapy in Khartoum State. The study included 50 patients under hormone therapy and was carried out in Khartoum State, Sudan, among women who underwent hormone therapy.
Study Sampling
Buccal smear samples were collected from one hundred participants to prepare for staining with H&E stain using wet and dry methods.
Sample Collection
Collect one buccal smear from the buccal mucosa of patients undergoing hormone replacement therapy using a tongue depressor after washing the mouth to avoid contamination by bacteria.
Sample Procedure
For wet fixed smears, the smear was taken using the brush method and stained in Mayer’s hemalum solution for 3 minutes, then rinsed in 0.1% HCl solution for 2 seconds. The slide was differentiated in running tap water for 3-5 minutes, then stained in 0.5% aqueous solution of eosin Y for 3-5 minutes, rinsed in tap water for 3 seconds, in an ascending alcohol series, Xylene was applied, then the smear was mounted in DPX.
Dry Smears
Slides were allowed to air dry for several minutes to remove moisture, then stained with filtered 0.1% Mayer’s Haematoxylin for 10 minutes in a 50ml conical tube in a Coplin jar, slides were rinsed in cool running water for 5 minutes. The slides were then stained in 0.5% eosin (1.5g dissolved in 300ml of 95% ethanol) for 12 times, dipped in distilled water until the eosin stopped streaking, applied in 50% ethanol for 10 minutes and in 70% ethanol for 10 minutes, equilibrated in 95% ethanol for 30 seconds, and equilibrated in 100% ethanol for 1 minute. Finally, the slides were dipped in Xylene several times, mounted, and cover slipped for examination.
Statistical Analysis
After examining the smears under a microscope, the results of the laboratory investigation as well as demographic data from the patients will be processed using the Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS).
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Ethical approval was obtained from the Gharb El-Niel College Ethical Research Committee in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki Principles, and agreements were obtained from hospital administrations before sample and data collection. Patient information was highly secured and not used for purposes other than scientific inquiry.
Ethical clearance code number: GE-RES/04-022-06
Date: 8/1/2022
Results
Distribution of the patients according to age
|
Age |
Number |
Percentage % |
|
20-25 years |
6 |
12.0 |
|
26-35 years |
14 |
28.0 |
|
36-45 years |
21 |
42.0 |
|
45-50 years |
9 |
18.0 |
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
Distribution of the patients according to educational level
|
Educational background |
Number |
Percentage % |
|
Illiterate |
9 |
18.0 |
|
Primary |
11 |
22.0 |
|
Secondary |
16 |
32.0 |
|
University |
14 |
28.0 |
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
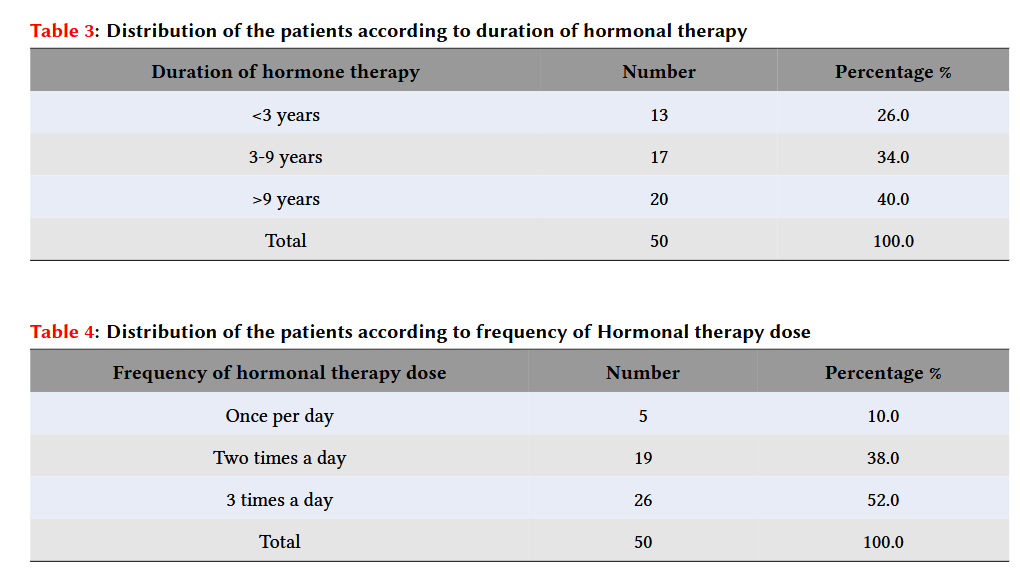
Distribution of the patients according to duration of hormonal therapy
|
Duration of hormone therapy |
Number |
Percentage % |
|
<3 years |
13 |
26.0 |
|
3-9 years |
17 |
34.0 |
|
>9 years |
20 |
40.0 |
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
Duration of the hormonal therapy received by the patients is shown in
Distribution of the patients according to frequency of
Hormonal therapy dose
|
Frequency of hormonal therapy dose |
Number |
Percentage % |
|
Once per day |
5 |
10.0 |
|
Two times a day |
19 |
38.0 |
|
3 times a day |
26 |
52.0 |
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
Frequency of the hormonal therapy dose per day that received by thepatients is shown in
Distribution of the patients according to cytology results
|
Pathology |
Wet fixed smear |
Dry smear |
P value | ||
|
|
Number |
Percentage % |
Number |
Percentage % | |
|
Normal |
5 |
10.0 |
5 |
10.0 |
0.14 |
|
Inflammatory |
17 |
34.0 |
17 |
34.0 | |
|
Malignant |
28 |
56.0 |
28 |
56.0 | |
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
50 |
100.0 | |
As shown in
Distribution of the cytological results according to slide staining quality
|
Slide staining quality |
Wet fixed smear |
Dry smear |
P value | ||
|
|
Number |
Percentage % |
Number |
Percentage % | |
|
Excellent |
20 |
40.0 |
20 |
40.0 |
0.11 |
|
Very good |
14 |
28.0 |
14 |
28.0 | |
|
Good |
10 |
20.0 |
10 |
20.0 | |
|
Acceptable |
4 |
8.0 |
4 |
8.0 | |
|
Poor |
2 |
4.0 |
2 |
4.0 | |
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
50 |
100.0 | |
As shown in
Correlation between cytology results and duration of hormonal therapy use
|
Cytology results |
Duration |
P value | |||||
|
|
>3 years |
3-9 years |
>9 years | ||||
|
|
Number |
Percentage % |
Number |
Percentage % |
Number |
Percentage % | |
|
Normal |
4 |
30.8 |
0 |
0.0 |
1 |
5.0 |
0.001 |
|
Inflammatory |
8 |
61.5 |
9 |
52.9 |
0 |
0.0 | |
|
Malignant |
1 |
7.7 |
8 |
47.1 |
19 |
95.0 | |
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
50 |
100.0 |
50 |
100.0 | |
As shown in
Correlation between cytological results in relation to dose of hormonal therapy used per day
|
Cytology results |
Duration |
P value | |||||
|
|
1 |
2 |
3 | ||||
|
|
Number |
Percentage % |
Number |
Percentage % |
Number |
Percentage % | |
|
Normal |
2 |
40.0 |
2 |
10.5 |
1 |
3.8 |
0.002 |
|
Inflammatory |
2 |
40.0 |
13 |
68.4 |
2 |
7.7 | |
|
Malignant |
1 |
20.0 |
4 |
21.1 |
23 |
88.5 | |
|
Total |
50 |
100.0 |
50 |
100.0 |
50 |
100.0 | |
As shown in
Discussion
In this study, fifty Sudanese women who received hormone therapy were assessed based on cytological changes in buccal smears using wet fixed and dry H&E stains. A previous study suggested that patients exposed to cancer therapy exhibit poorer oral health 11. As shown in
In
Conclusion
The study concluded that the cytological results of buccal smears prepared by wet fixation and dry methods were more likely to be malignant, followed by inflammatory and normal findings. There were no significant differences in the cytological reports of the buccal smears prepared by dry and wet methods. Malignant buccal cells showed significant differences in the buccal smears according to the duration and frequency of hormone therapy use per day.
Abbreviations
HRT: Hormone replacement therapy
H&E: Hematoxylin and Eosin
SPSS: Statistical Package for Social Science
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
The data sets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Competing interests
Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding
Not applicable.
Authors’ contributions
FME and AAI conceived the design and carried out the experiments. FME obtained, analyzed and interpreted the data. FME and AAI wrote and revised the manuscript. AAI provides financial support for all experiments. All authors have critically reviewed and approved the final draft and are responsible for the content and similarity index of the manuscript.
Acknowledgements
Thanks for all participants involved in this research.

