Prognostic Value of Cardiac Troponin T, Cardiac Troponin I and CK-MB among Chronic Renal Failure
- Al-Ghad International College for Applied Medical Sciences, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- aculty of Medical Laboratory Science, Department of microbiology, Nile University, Khartoum, Sudan
- Faculty of Medical Laboratory Science, Department of clinical chemistry, Alneelain University, Khartoum, Sudan
- Ahfad University for Women, Sudan
Abstract
Background: Cardiac troponin T (cTnT) is a highly sensitive and specific marker of myocardial damage. The aim of this study was to investigate the prognostic value of a new sensitive TnT assay in comparison with TnI and other cardiac markers. Methods: We measured serial pre- and post-dialysis cTnT, cTnI, and creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB) concentrations in 100 patients with end-stage renal failure without signs of acute myocardial infarction. Sera were analyzed for cardiac troponin T (cTnT) using the Elecsys Analyzer 2010 immunoassay system and for cardiac troponin I (cTnI) using the Immulite automated immunoassay analyzer. Results: There were no significant differences in pre- and post-dialysis values for TnT and TnI (p ≥ 0.05), while CK and CK-MB levels were significantly lower post-dialysis (p ≤ 0.05). Elevated pre-dialysis levels above the upper reference limits were found in 35 patients (35%) with the TnI assay (p ≥ 0.05) and in 65 patients (65%) with the TnT assay (p ≤ 0.05). Conclusions: Elevated troponin T identifies a subgroup of ESRD patients who may be at increased risk of cardiac infarction, even among asymptomatic individuals.
Introduction
There is a high incidence of cardiovascular disease among patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), leading to poor prognosis. Cardiovascular disease accounts for half of all deaths, with approximately thirty percent caused by myocardial infarction1,2,3,4,5,6,7.
Cardiac troponins consist of three proteins: cTnC, cTnI, and cTnT, which interact with tropomyosin to form the troponin-tropomyosin complex8,9,10,11.
Cardiac troponin T (cTnT), measured in serum or plasma, is a highly sensitive and specific marker of acute myocardial damage12,13,14. Many factors have been associated with increased cTnT concentrations, such as age, diabetes mellitus, and coronary artery disease, but the specific mechanisms remain unclear15,16,17,18,19. This study aimed to investigate the use of cardiac troponin T (cTnT) as an early marker for myocardial infarction (MI), and to compare the diagnostic accuracy of cTnT with cTnI and CK-MB among chronic renal failure patients.
Methods
A total of 100 consecutive ambulatory and in-hospital chronic renal failure (CRF) patients undergoing long-term hemodialysis at hemodialysis centers in Khartoum state, Sudan, were included in the study. Patients were followed up for 12 months for all-cause mortality, cardiac mortality, and new nonfatal cardiovascular disease (AMI, unstable AP). This prospective study was approved by the research ethics board and postgraduate council of Elneelain University. Blood was collected from the patients after a 3-day interval of non-dialysis at the onset of the study and 4 weeks, 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year later.
cTnT was measured by an automated random access multichannel analyzer Elecsys analyzer 2010 immunoassay system. The analyzer is specially designed for performing assays utilizing electrochemiluminescent (ECL) technology20. cTnI was measured by the Immulite automated immunoassay analyzer that performs chemiluminescent immunoassays automatically21,22. Creatine Kinase (CK MB) isoenzyme mass was determined by fluorimetric enzyme immunoassay (Stratus II, Dade Berhing), an antibody to anti-CK MB inhibits completely CK MM and subunit M of the CK MB. The activity of the non-inhibited CK B subunit is then assayed by a series of reactions20. Cardiac events included admission for unstable angina, acute myocardial infarction, diagnosed by electrocardiogram (ECG) changes, echocardiography, angiography, or autopsy, and sudden death.
Statistical Analysis
Values are presented as the median and 25–75 percentile. The paired t-test was used to compare pre- and post-dialysis results. Sensitivity and specificity for predicting 12-month events were calculated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. Correlations between TnT, TnI, CK-MB levels and the patient's age and time on dialysis were performed to calculate the relative risks for the respective 12-month events, and significance was set at p ≤ 0.05.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
All participants were fully informed about the aims and outcomes of the study and were asked to sign a written consent form before specimens were collected by the pathologist in charge. The results were shown to and discussed with the patients. Ethical approval was obtained from the Elneelain University Ethical Research Committee in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki Principles, and consent was obtained from all patients before sample and data collection. The patients’ information was highly secured and not used for purposes other than scientific inquiry. Risks and benefits for the patients resulting from the research outcomes were ensured. Approval reference number: ELN-REC/03-022./09. Approval date: 20/1/2022.
Results
A total of 100 chronic renal failure patients attending different dialysis centers in Khartoum state were enrolled to assess the diagnostic power of myocardial markers (cTnT, cTnI, and CK-MB). The clinical characteristic data of our study subjects are shown in
Outcome
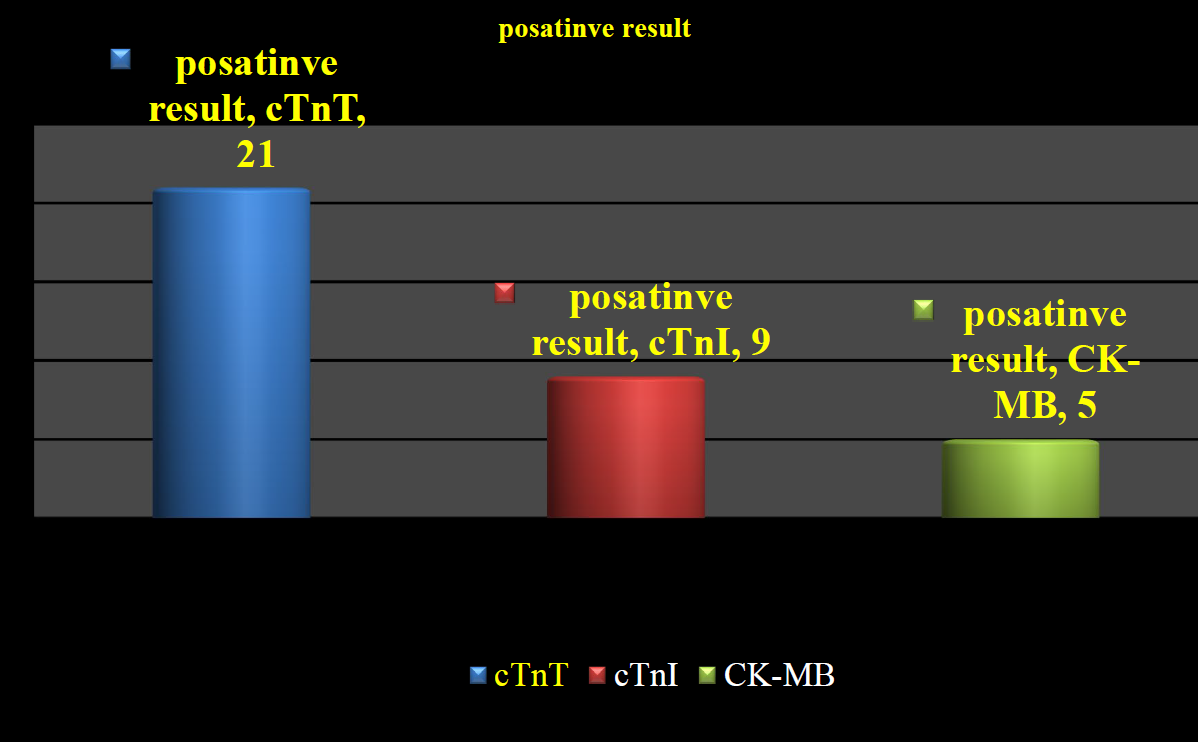
During the 12-month follow-up period, 35 patients (35%) experienced cardiac events, and two patients (2%) died. Patients without 12-month events numbered 63 (63%). Among the 35 patients with cardiac events, TnT showed positive results (> 0.1 ng/ml) in 21 patients (60%), while 9 patients (25.7%) had elevated cTnI (> 1.0). CK and CK-MB mass were positive in 5 of the 35 patients with cardiac events (14%) (
Clinical characteristics of the study population(n = 100) at baseline
| Variable | No.of patients(%) |
|---|---|
| Sex |
Male 69 (69), Female 31(31) |
| Age in years |
10 – 19 3 (5) 20 - 29 11(11) 30 – 39 14 (3) 40 – 49 23(23) 50 - 59 25(25) 60 – 69 13(13) 70 – 80 11(11) |
| Length of time on dialysis in years |
1 – 2.9 37(37) 3 – 4.9 24 (24) 5 – 6.9 15 (10) 7 – 8.9 3(3) 9- 10.9 7(7) 11- 12.9 6(6) 13 – 14 8(8) |
|
Body mass index [kg/m2] Mean(range) | 22.7(19.4- 26.1) |
|
Renal diagnosis Diabetes Glomerulonephritis Isckeamic Obstructive/CPN Hypertensive Unknown 0thers |
18 (18) 18(18) 12(12) 13(13) 16 (16) 17(17) 6 (6) |
Assay results of cardiac markers (median and interquartiles) prior to and 4–6 h after dialysis
| Prior to dialysis | 4–6 h after dialysis | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Troponin I (μg/l) |
0.12 (0.06–0.19) |
0.13 (0.07–0.20) | ≥ 0.05 |
| Troponin T (μg/l) | 0.063 (0.023–0.154) |
0.061 (0.027–0.158) | ≥ 0.05 |
| Creatine kinase (U/l) |
33.5 (23.0–66.5) |
32.0 (20.0–54.5) | ≤ 0.05 |
| CK-MBmass (μg/l) | 0.67 (0.21–1.53) |
0.50 (0.11–1.15) | ≤ 0.05 |
laboratory data in patients with and without cardiac events
| (30-39) | (40-49) | (50-59) | (60-69) | (70-80) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cTnT | 0 | 1 | 7 | 5 | 8 |
| cTnI | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 5 |
| CK-MB | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 |
showing duration and result of cTnT, cTnI and CK-MB
| Patients with events n = 35 | Patients without events n = 63 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Troponin I (μg/l) |
0.1 (0.0–0.2) |
0.1 (0.0–0.2) | ≥ 0.05 |
| Troponin T (μg/l) |
0.13 (0.05–0.26) |
0.05 (0.02–0.10) | ≤ 0.01 |
| Creatine kinase (U/l) | 31 (20–58) |
39 (25–76) | ≥ 0.05 |
| CK-MBmass (μg/l) |
0.85 (0.35–1.87) |
0.60 (0.18–1.01) | ≥ 0.05 |
showing Age distribution and result of cTnT, cTnI and CK-MB
| (1-1.9) | (2-3.9) | (4-5.9) | (6-14) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cTnT | 2 | 12 | 4 | 3 |
| cTnI | 1 | 7 | 1 | 1 |
| CK-MB | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
Correlation of cardiac markers levels with patients age and the duration of dialysis in the study subjects
| Variable | Statistic | Age in years | Duration of dialysis in years |
|---|---|---|---|
| Troponin T | Person correlation | 0.34 | 0.37 |
| Significant (p) | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
| Troponin I | Person correlation | 0.39 | 0,42 |
| Significant (p) | 0.02 | 0.01 | |
| Creatinine kinase | Person correlation | 0.019 | 0.05 |
| Significant (p) | 0.3 | 0.7 | |
| CK-MB | Person correlation | 0.06 | 0.015 |
| Significant (p) | 0.68 | 0.54 |
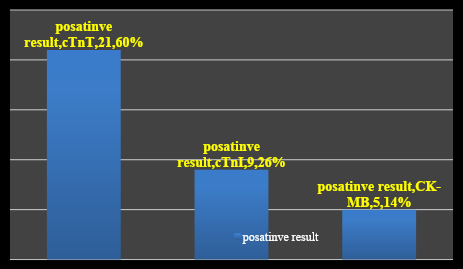
showing positive result of cTnT, cTnI and CK-MB.
Discussion
Prior to the introduction of the cardiac troponin assay, cardiologists used total creatine kinase, the MB isoforms of creatine kinase (CK-MB), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) isoforms to assess myocardial damage. These markers had serious analytical and clinical limitations; consequently, researchers sought other markers to improve the diagnosis of myocardial infarction. These studies confirm that troponin T demonstrates improved sensitivity and specificity when compared to other biochemical markers among hemodialysis patients. The present study was designed to determine the levels of the cardiac markers troponin T, troponin I, and creatine kinase (CK-MB), which is in agreement with previous reports23,24,25,26. Our study showed a remarkable increase of cTnT in ESRD compared to cTnI and CK-MB by 28%, 12%, and 6.7%, respectively, which is in accordance with previous findings27,28,29,30,31. This study showed that there is a relationship between the duration of dialysis and the elevation of cTnT. Our results also revealed that aging significantly affects the cardiac markers. The study population was entirely from residential areas in Khartoum State, excluding other Sudanese states.
Conclusion
Elevated troponin T identifies a subgroup of ESRD patients that may be at increased risk of cardiac infarction among asymptomatic individuals, whereas troponin I and CK-MB mass have poor prognostic value.
Abbreviations
CK MB: Creatine Kinase CRF: Chronic renal failure cTnT : Cardiac troponin T ECG: Electrocardiogram ECL: Electrochemiluminescent ESRD: End stage renal disease MI: Myocardial infarction
Acknowledgements
Thanks for all participants involved in this research.
AUTHOR’S CONTRIBUTIONS
AAO and NAO conceived the design and carried out the experiments. AMA obtained, analyzed and interpreted the data. NAO and AAI wrote and revised the manuscript. AAI provides financial support for all experiments. All authors have critically reviewed and approved the final draft and are responsible for the content and similarity index of the manuscript.
FUNDING
None.
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS
Data and materials used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.

